Safety Quizzes
Level up your safety knowledge and pick up some proficiencies to boost your profile! Check out the safety quizzes, compliments of our community.

Quiz Quetion - Fall Protection
I am the safety person in a US Shipyard on the Great Lakes. On the USS Fitzgerald that we are building in our yard the fall protection threshold for employees is ___ feet?

Quiz Quetion - Fall Protection
I am the safety person in a US Shipyard on the Great Lakes. On the USS Fitzgerald that we are building in our yard the fall protection threshold for employees is ___ feet?

Tool Box Talk
What is the primary purpose of a Toolbox Talk (TBT)?

Lithium-Ion Battery Hazards in the Workplace — Knowledge Check Day Ten
10. Which of the following actions helps prevent reignition after a lithium-ion fire? Day Nine Question/Answer 9. Under the EPA’s Universal Waste Rule, used lithium-ion batteries must be: Answer: B - Stored, labeled, and sent to certified recycling or disposal facilities. Explanation: The Universal Waste Rule requires safe labeling, storage, and transport to certified facilities — not landfill disposal.

Lithium-Ion Battery Hazards in the Workplace — Knowledge Check Day Nine
9. Under the EPA’s Universal Waste Rule, used lithium-ion batteries must be: Day Eight Question/Answer 8. What type of fire extinguisher or system is generally recommended for lithium-ion battery fires? Answer: A – Large Amounts of Water Explanation: Large amounts of Water is the best answer based on current knowledge and should be applied by the Fire Department in Full Turnout Gear. While Class D or clean agent systems can safely suppress lithium fires and prevent re-ignition; CO₂ and Foam are not the best to use. Note: there are additives for the water that are being advertised as effective, but this is if they can get through the battery box and on the cells. Typically, the battery boxes are waterproof, so this is difficult to get the agent on the cells.

Lithium-Ion Battery Hazards in the Workplace — Knowledge Check Day Eight
8. What type of extinguishing media that is generally recommended for lithium-ion battery fires? Day Seven Question/Answer 7. According to good practice, where should lithium-ion batteries not be stored? Answer: B - Near heat sources or direct sunlight. Explanation: Heat exposure accelerates degradation and increases fire risk. Batteries should be stored in cool, dry, ventilated areas.

Lithium-Ion Battery Hazards in the Workplace — Knowledge Check Day Seven
7. According to good practice, where should lithium-ion batteries not be stored? Day Six Question/Answer 6. Which control is considered an engineering control for lithium-ion battery hazards? Answer: B - Installing fire-rated, ventilated battery storage rooms. Explanation: Engineering controls physically change the environment (e.g., fire-rated rooms, ventilation, suppression systems).

Lithium-Ion Battery Hazards in the Workplace — Knowledge Check Day Six
6. Which control is considered an engineering control for lithium-ion battery hazards? Day Five Question/Answer 5. What is the first step when a lithium-ion battery begins to overheat, vent, or smoke? Answer: C - Evacuate and isolate the area, then notify emergency personnel. Explanation: Safety first — evacuate, isolate, and alert responders. Only trained personnel should manage thermal runaway events.

Lithium-Ion Battery Hazards in the Workplace — Knowledge Check Day Five 5.
Day Four Question/Answer 4. During a lithium-ion battery fire, which gas is of particular concern due to its extreme toxicity? Answer: C - Hydrofluoric acid (HF) Explanation: The electrolyte decomposes into hydrofluoric acid (HF), a highly toxic and corrosive gas that can cause severe injury. Day 5 Question: What is the first step when a lithium-ion battery begins to overheat, vent, or smoke?

Lithium-Ion Battery Hazards in the Workplace — Knowledge Check Day Four
4. During a lithium-ion battery fire, which gas is of particular concern due to its extreme toxicity? Day Three Question/Answer 3. Which of the following can trigger lithium-ion battery failure? Answer: D - All of the above; Physical impact or puncture, Overcharging or deep discharge and Exposure to excessive heat or moisture Explanation: All listed conditions can damage internal separators or cause short circuits, leading to fire or explosion.

Lithium-Ion Battery Hazards in the Workplace — Knowledge Check Day Two 2.
What is thermal runaway in a lithium-ion battery? Day One question/answer 1. Which of the following best explains why lithium-ion batteries present higher hazards than most other rechargeable batteries? Answer: C - They store large amounts of energy in a small volume. Explanation: Lithium-ion batteries have very high energy density, which increases the potential for fire or explosion if damaged or mishandled.

Lithium-Ion Battery Hazards in the Workplace — Knowledge Check Day Three
3. Which of the following can trigger lithium-ion battery failure? Day Two Question/Answer 2. What is thermal runaway in a lithium-ion battery? Answer: B. When internal heat causes a self-sustaining reaction leading to fire or explosion. Explanation: Thermal runaway is an exothermic chain reaction — heat causes internal reactions that generate even more heat, potentially igniting the cell.

Lithium-Ion Battery Hazards in the Workplace — Knowledge Check
Over the next several days I will be adding a question and will provide the previous questions answer with the next day's question! Good Luck! 1. Which of the following best explains why lithium-ion batteries present higher hazards than most other rechargeable batteries?

Fire Hydrant Color Codes
Per NFPA 291, what color fire hydrant flows the most water?
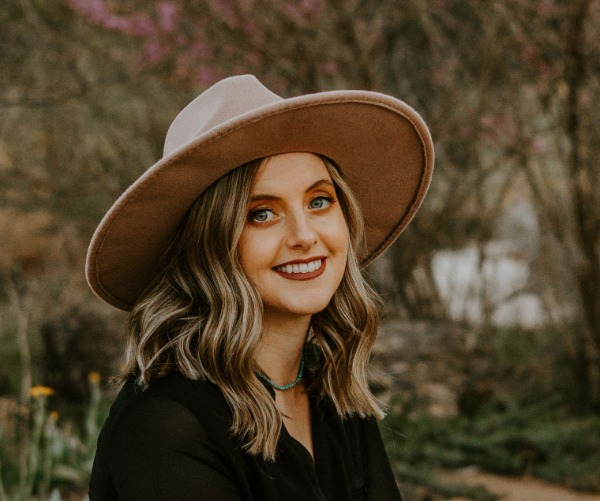


Electrical Gloves - Ready to Use?
Today, September 26, 2025, an electrician inspected and conducted the inflation test on these electrical rubber-insulated gloves. They were in good condition. After the test and inspection, he put his leather gloves over them. According to 29 CFR 1910.137, are the electrical rubber-insulated gloves ready to use (see photo)? Answer Yes or No and then comment, why or why not! I will put the answer in the comments!


NFPA 704 - Special Hazards
Per NFPA 704, which of the following is NOT an approved symbol that can be in the white section of the NFPA 704 marking system?

Electrical Safety
Which type of fire extinguisher is most suitable for electrical fires ?

Return-To-Work
A team member is re-entering the workforce after time off through worker's compensation. The previous position has been left open to accommodate the team member upon return. However, the team member now states (due to long term recovery needs) expectations for the previous position cannot be met. Is the employer responsible for ensuring employment?
Ergonomics
What is the best way to lift heavy objects safely ?
AI in OSH
What is a potential drawback of integrating AI into OSH practices?